Key concepts of Compliance Maps
This section allows you to explore and learn the key concepts behind Compliance Maps.
Relationships in Compliance Maps
The following illustration depicts the relationships between regulations or standards, requirements, and controls in Compliance Maps.
Note
- Interface terms are customizable, and fields and tabs are configurable. In your instance of Diligent One, some terms, fields, and tabs may be different.
- If a required field is left blank, you will see a warning message: This field is required. Some custom fields may have default values.
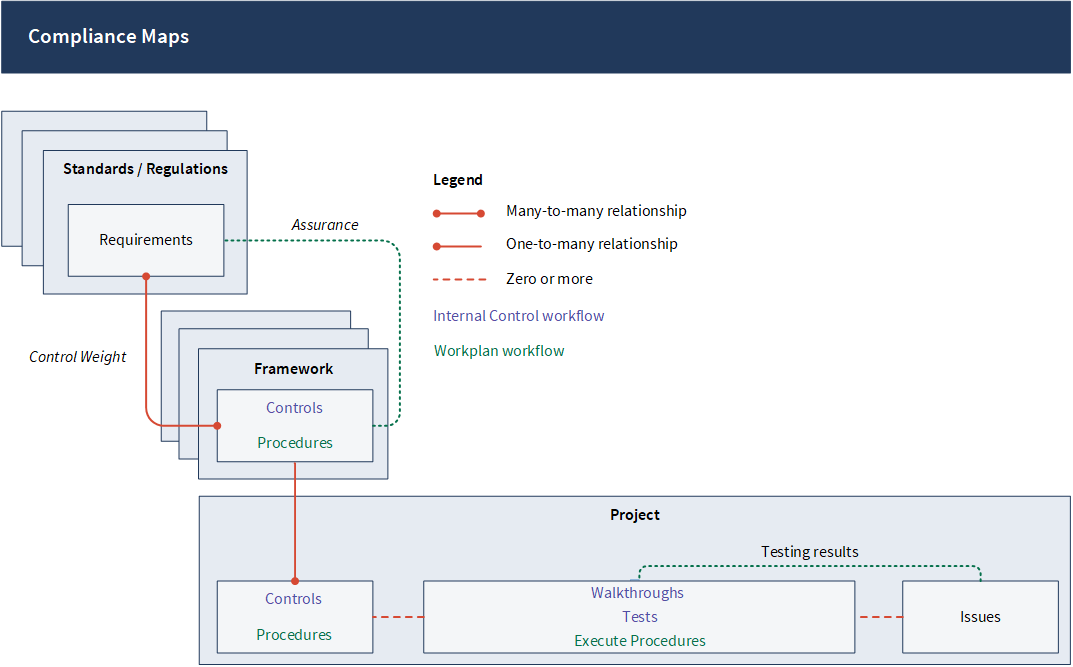
Terms
The following list defines the terms used in Compliance Maps:
- Regulations Authority documents that are written and issued by federal government departments, often categorized under an act.
Examples
FedRAMP 2016 0.1
Green Book - Revision 2014 (GAO-14-704G)
NIST SP 800-53 Security Controls - Rev4
- Standards Authority documents that are sources of best practice requirements and related citations.
Examples
COBIT 5 Framework
Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard
COSO Internal Control Framework 2013
-
Requirements A series of directives that have been established to summarize a standard or regulation.
NoteAlthough requirements may be referred to as principles, attributes, activities, tasks, or steps in different regulations and standards, the common term used in Projects is Requirement.
Examples
- Establish and perform backup procedures for applications, databases, system configurations, network configurations, documents, and messaging systems.
- Document the concept of operations in the continuity plan, including a system description, line of succession, and responsibilities.
-
Controls Measures or courses of action for assuring the achievement of an organization's compliance with requirements.
Examples
- Policies and procedures related to data backup are in place which make employee responsibilities clear and actionable.
- Real-time data replication between servers is done in order to provide a "hot" backup should the core production system fail.
- Applicable The indication of whether or not the requirement is relevant or appropriate for your organization.
- Covered The indication that the requirement is met.
- Control Weight The percentage of the requirement that the control covers.
- Coverage A percentage measurement that indicates the extent to which applicable requirements have been indicated as "covered."
- Gaps A count of the number of applicable requirements that are not covered.
- Assurance A calculation that represents your organization's confidence in requirements being met.
Benefits for different professionals
| Professional title(s) | Benefits |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|